Poultry production in Thailand
Currently, Thailand is raising layer chickens. Widespread both natural and industrial culture. which the area is an important source of chicken egg production Thailand is mainly in the eastern region. followed by the Northeast, the North, the Central, the South and the West Bangkok and its vicinities, respectively. The provinces that produce the most eggs are Chachoengsao Province. followed by Nakhon Nayok Province Chonburi, Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya and Ubon Ratchathani, respectively.
Laying hens
Chicken breeding is an important factor in the successful chicken farming business. so the babysitter Must choose the chicken breed according to the purpose of raising, such as choosing chicken breeds for egg production, etc. In the past, it was popular to raise purebred chickens, but the egg breeds that are popular in Thailand today are mostly chicken breed Almost all hybrids Which is a breed that has been selected and bred as well, such as fertilizing eggs, growing eggs, laying eggs, resistant and eating less food. There are 3 types of chicken breeds raised in Thailand as follows:
Purebred chickens are the chickens that have been selected and bred continuously by breeders until Successive offspring are similar in shape, size, color, etc. to their ancestors or fixed breed characteristics. Purebred chickens were once very popular. Because it is known as a hen that lays eggs. But later it has been improved. Breeding breeds with higher yields instead of purebred chickens have become less popular. Until now, the chicken breed Has received little attention and is a commercial party. Because laying hens are popular with raising chickens from hybrids. Cross-breeding, which produces much better yields than purebred chickens. As for the purebred layer chickens that are still kept in Thailand, they are:
1.1 Rhode Island Red breed, also known as “Road Chicken”, originated live in the united states It is an old breed of chicken that is more than 100 years old by breeding and selection. from red Malay chicken Red Shanghai Chicken Brown horned hens, Cornis hens, Wyyan dots and Brahmas breed chickens. There are two types of Rhode Island Red, namely the rose comb type and the crested chakra (single comb). Which is a chicken that gives quite good eggs used to have a record of winning the egg-laying competition in Thailand is always
Characteristics of Rhode Island Red Crest Chak Chicken It is a semi-meat and semi-egg chicken. has been bred until there is a crest medium-sized crest It is quite long and deep. rectangular The general feathers on the body are brown, dark red, and the wing feathers and tail feathers are black and green. The skin and shins are very yellow. red-yellow mouth, red eyes, crest
Chakra 5-pointed, ear pads are red. The eggshell is brown. Medium-sized eggs, docile character, able to adapt to The environment is good. Egg laying begins at about 5 and a half months of age. Eggs are quite fecund, i.e. 280-300 eggs per year. Body weight when mature. Male weighs 3.1-4.0 kg. Female weighs 2.4-4.0. kg
In the past, in Thailand it was very popular to raise chickens of this breed. because in addition to yielding good results in both eggs and meat Strong, resistant, easy to raise and grow fast, but nowadays popular for use as a breeding ground in the production of hybrid laying hens Mostly hybrids To obtain a hybrid that can be gendered at birth by using a male Rhododendron mixed with a bar. Plymouth Rock Female The resulting hybrids can be sexed at 1 day of age by looking at the difference in the color of the feathers, that is, the female chicks have black hair throughout the body.
The male chicks have black feathers all over the body but have a white spot on their heads and when fully grown, the female hybrid chickens are the chickens that have all black feathers. And the male hybrid chickens will have colored feathers throughout the body like a chicken. Bars by today’s commercial laying hens that provide brown-shelled eggs are Mainly from the crossbreeding of chickens. Rhode Island Red Crest with Bar Plymouth Rock Chicken The resulting hybrids will fertilize eggs. Eggs have brown shells and produce large eggs.
1.2 Barred Plymouth Rock breed, also known as “Chicken Bar”, is a Plymouth Rock chicken with bar colored feathers. It has black and white hairs alternating across the hair shaft, long body, crest, yellow mouth, reddish-brown eyes. The crest and earrings are red, the skin is yellow, the legs and toes are red. give brown-shelled eggs Start laying eggs at about 5 and a half months of age. Tolerant of environmental conditions. Males weigh about 3.6-4.3.
kg. Females weigh about 2.7-3.7 kg.
The Bar Plymouth Rock chicken breed originated in the United States. It is a semi-meat and semi-egg chicken. is a species Has been bred and selected around the year. 1865 by crossing Dominic male hen (Dominiqlue) and female hen Black Chochin (Black Java) used to be bred. The popularity of raising as laying hens for a while, about 30 years ago, but nowadays the mother is used to mix with the breeder. Rhode Island Red or New Hampshire breeds to produce hybrids are commercially selective, gender-selective at birth based on coat color, with females having black fur and fertile eggs. The male hybrids have a bar color.
1.3 Single Comb White Leghorn breed originated in Italy. It is the most popular breed that is widely kept among the small horn chickens together. This breed of chicken used to be popular as a chicken. eggs widely In the early days, there was an industrial laying hen. It is a light chicken breed that is small, agile, agile, has a fast growth. Full white fur, large 5-pointed crest, red crest, yellow mouth, white earrings, yellow skin and hard face, ovulate quickly, fertilize, white shell eggs. effective in The change in diet is quite high. Tolerant of hot weather, start laying eggs at the age of about 4 and a half months, laying about 300 eggs per year, weight at maturity, males 2.2-2.9 kg, females 1.8-2.2 kg.
Currently, the white-horned, crested small-breed chickens are commonly used to cross breed 2 or more breeds. to produce chicken eggs Commercial hybrids that fertilize, grow eggs, and eat less. which meets the market demand
Hybrid Breeds (Hybrid Breeds) refers to laying hens that are produced by mixing two or more breeds of laying hens together. Because it is a specially mixed breed of chicks, the egg production company has developed and improved the breeding to be effective in yielding. Egg production is high and the quality meets the market demand, namely the fertilization of eggs. brown eggshell Large eggs and resistant eggs because it has been gathered together
This hybrid chicken has characteristic traits and includes detailed breeding information such as growth rate, feed intake. survival rate Ovulation percentage The length of time for laying eggs, the size of the hens. The size of the egg, the color of the eggshell, etc., but this hybrid chicken must be fed with high-quality food. There is proper management such as weight control. food intake control lighting control throughout the sanitation and Good disease prevention as well.
As most of the hybrid chickens are bred by commercial layer breeding companies, the company will keep the source chickens and the breeding system confidential. for commercial benefits chicken present There are many hybrid eggs. Most of them were bred in the United States and in Europe. with a specific copyright In Thailand, private companies have imported broiler, grandparent and parent chickens. Produce chicks and eggs for sale to breeders There are many varieties, such as AA Brown, Ross Brown, Hisex Brown, Isa Brown, Super Hard. Super Harco, Dekalb Voren, Hubbard Golden Commet, Shaver Starcross 579, Babcock B-380 (Babcock B-300), Babolna Tetra-SL, etc.
Principles for choosing a breed of laying hens to raise
Because chicken breed is one of the important factors in raising layer chickens successfully. Therefore, the selection of varieties Laying hens must be carefully considered. Don’t be fooled by the advertisements alone. The breeder must select the breed. By using observations and based on the following criteria for consideration
It is a good selection of chickens that have been specially selected as laying hens.
Looks good according to the breed and type of laying hens.
Produced from farms of good and reliable standards
High efficiency in egg production Long peak egg period, resistant eggs, large eggs and thick shells. 5. Has a high survival rate, is strong and can withstand the weather conditions of Thailand well. are considered and other varieties for comparison.
Structure of the Egg
The structure of an egg is made up of five major components: the egg shell and egg shell membrane, air cell, air space, egg white (albumen), egg yolk (yolk). ) and the origin (Germinal dise) as shown in Figure 1.
Shell The eggshell consists of two important layers within these layers. with many pores about 8, 000 Holes for passage of water and gas. In addition, bacteria May pass or penetrate through the holes in the eggshell as well. The newly released eggshell is usually clear, but becomes opaque when it dries. The outer surface of the eggshell is covered by a thin membrane called (Bloom or cuticle). After the egg comes out, this thin membrane dries quickly, causing it to close the pores in the shell completely. to prevent evaporation of water and gas from the eggs as well as to prevent the penetration of bacteria that may occur in the shell of the fish. The egg shell is more porous than the rest of the eggshell. During approximately 3 weeks of incubation of the mother egg, approximately 15% of the egg shell’s thickness has been evaporated by moisture or water. visible that is directly related to the volume of eggs for example A hummingbird’s eggshell is only 0. 06 mm The eggshell needs to be thick enough to hold the components inside the egg and to be brittle. enough to allow the embryo to penetrate easily.
gradually decreased, resulting in the components inside the egg to contract more than the egg shell, causing the inside of the egg to be Vacuum and air are drawn through the perforations at the obtuse end of the egg, thus creating air pockets. The size of the air pockets will increase over time. (Especially in hot and dry areas) The enlargement of the air pockets occurs from the evaporation of water and gas from the egg bubbles. Function to prevent shock that may occur from shock (Shock absorber) during embryonic development. within the first It is also the part that provides air for the embryo inside the egg that has incubated 21-28 days, which it will use its beak to penetrate the membrane of the egg to understand the air space inside the new egg to notice the white terminal part 2. Terminals are attached at both ends of the yolk (White cords). These terminals are called chalazae, which are twisted strips. Twisted strands of mucin fibers Contains proteins This special kalasa serves to hold the yolk in the middle of the egg.
Egg White (The White or Albumen) Egg white is a half-solid, half-liquid protein. rather contain high water content. Flexible, acts as a shock absorbing and heat shield as well. The white meat can be divided into four layers: (1) Outer thin white (Layer of outer thin white or Fluid layer) (2) Middle thick white layer (Layer of thick white) (3) Inner liquid layer (Layer of inner thin white) and (4) Chalaziferous layer (Layer of thick white) which surrounds the egg yolk layer. in the end of the egg white at both ends side of the yolk It is shaped like a knot, resulting in a part called chalaza, which serves to hold the egg. Red is in the middle of the egg and allows the yolk to spin and twist around, the rest is Non protein solids.
The yolk The yolk is made up of layers that are dark and lighter, stacked in a circle spread out. The radius is within the yolk membrane. (Vitellinemembrane) is usually lighter than egg whites. and often stays above the point At the center of the newly released egg, the germ cell (blastoderm) is seen as a faint spot on the top surface. noticeable This fertilization point in an egg that has been fertilized with a male fertilizes and develops.
Origin or growth point (The Germinal Disc) when hammering out the egg. will find that the skin On top of the yolk there is a white dot. which has a diameter of about 4 mm. The merger between one cell of the female gamete, or egg, and one cell of the germ cell. male or sperm Each cell contains only half the number of chromosomes (n) of normal somatic cells. The number of chromosomes is even (2n), and after the fusion of the egg and the sperm which is called the process Fertilization is a body cell with an even number of chromosomes (2n). Then the cell divides into 2 cells and continues to develop and divide. And the final result will develop into a chick further, in which the chicks, while inside the egg, rely on the elements inside the egg as food for growth.
Chemical composition of the egg (Composition of the Egg)
Most of the ingredients of an egg are Water and equal amounts of protein, fat and ash. The yolk is the part The highest nutrient concentration was only 50 percent water, as shown in
egg storage
The purpose of egg storage is to minimize the changes in the composition of the egg. It slows down the growth of microorganisms and maintains the water and carbon dioxide content in the eggs for as long as possible. Usually, whole eggs can be stored for a long time. because there is an egg shell as a protection Therefore, keeping the quality Eggs should be started by collecting eggs in the coop as often as possible. To prevent cracking and reduce microbial contamination, there are How to store eggs as follows:
– Store at low temperature at 11.6 – 14.4 °C for commercial eggs and 17.2 – 20 °C for laying hens.
– The relative humidity is about 75 – 80 percent, if the relative humidity is more than 90 percent, it will cause mold.
– Eggs are kept in a condition containing 0.55-2.5% CO2 – Coat the eggs with mineral oil and process them into salted eggs. or scrambled eggs
Egg shape
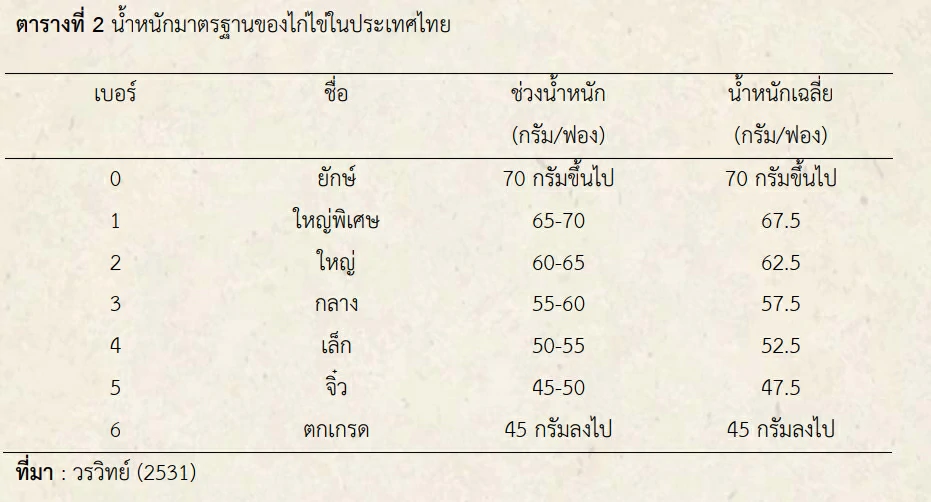
Eggs are normally oval-shaped, with air pockets slightly more obtuse than the other, but sometimes eggs are found to have irregular holes as well, such as rounded or elongated, distorted, the surface of the bubbles. Eggs, rough, wavy, etc. by standard weight of laying hens in Thailand. Shown in Table 2. Table 2 Standard weight of layer hens in Thailand.
Textures that appear on the eggshell, such as white, grey, cream, brown, red, or green It appears that the eggs of There are many types of birds that will have streaks. speckled stain Or it can be bands of brown, red, lavender, gray, black, and other colors as well.
Factors that differentiate the size of the fever
The size of laying hens is usually in the weight range of 45-65 g. Several factors include:
Breed Chicken (Breed) The size of the egg is a trait controlled by genetics that can be passed on to offspring.
Characteristics of chickens (Individual) in the same breed of chicken, different breeds or chickens, but each chicken will give eggs of different sizes And even if the same breed of chicken, when the given environment changes, will produce eggs of the same size. vary with
The age of the chicken (Age of bird). Chickens that begin to lay new eggs. That will give the eggs that are small first. and when the chicken is old The more eggs, the larger the eggs.
Temperature (Temperature) In a higher temperature environment, the hens produce smaller eggs. because the hens eat less food If the temperature is lower, the hens will produce larger eggs.
Type of housing: Liver caged chickens produce larger eggs than traditional chickens. Approximately 14 g of ground is released per dozen eggs, and slated hens produce larger eggs than hens raised on slats. Raised on the substrate
Feed and water The hens are fed a complete and nutritious diet. If the hen is not receiving enough water due to too hot or too cold water or unpalatability, or lack of water will result in the eggs being small and also resulting in decreased egg production.
Diseases Some diseases, such as Newcastle and Infectious bronchitic, have reduced egg production. The egg size is smaller and the eggs are often deformed. With chronic bronchitis, hens produce smaller eggs.
Grain fumigants, such as ethylene dibromide, have resulted in chickens producing significantly smaller eggs.
The order of eggs in the ovum (Clutch order) The sequence of eggs in the ovum affects the weight of the egg, which is the egg. The first egg in the liver is the largest, and the size of the next egg is correspondingly smaller in the size of the egg in the liver.
Number of eggs given that year Usually the chickens that give new eggs. It gives a small egg first and then the size of an egg bubble. Next, it will be larger. up to the standard for a long time Subsequently, as the chickens get older, their eggs tend to become smaller and smaller, respectively.
Age of the hen that gave the first egg The late laying hens will produce standard sized eggs faster than the hens. that gives the first egg faster
Egg abnormality
Sometimes the hen will give the same unusual eggs. Characteristics that are considered to be abnormal eggs that are often seen in laying hens are as follows:
Double-yolked eggs are formed due to abnormalities in egg development and ovulation. If two yolks develop at the same time and ovulate at the same time, they are called twins. It depends on the hens starting to lay eggs because the egg production system is not working properly.
Blood spots are formed in the egg because at the time of ovulation there are capillaries in the sac. Egg shell or egg laying at the beginning is torn with blood coming out. When an egg is formed in the fallopian tubes, there is also a blood spot in the egg. It is often found in eggs from high-yielding hens.
Meat spots occur in eggs due to the fact that during ovulation, part of the egg sac is broken. down with egg yolk It is usually a dark spot. The appearance of blood spots or flesh spots in the egg is a characteristic that can It is hereditary and we can improve chickens to avoid this trait by breeding these two traits. The economic importance of laying hen production is also very high.
Yolkless eggs are formed due to the presence of foreign objects in the fallopian tubes. The rest of the egg will then continue to form without the yolk in it. Normally, eggs without yolks are always smaller than normal eggs. It is sometimes called a “stone egg”.
Dented eggshell occurs because the first egg sometimes stays in the Uterus longer than usual and the hen has not yet laid eggs, while the next one is formed when the new one is fertilized. Build until the Uterus will hit the first egg, which already has a hard shell. When the egg after the egg has been created, it will Looks like a wrinkled part of the egg.
egg without shell Soft-shelled eggs are formed due to the absence of the outer shell covering the eggs. This may be due to the lack of certain nutrients needed for the absorption of calcium by the body: Vitamin D or calcium deficiency, which is necessary for the formation of eggshell calcium carbonate, or is often seen in animal stresses, such as after vaccination. Will cause abnormal egg production process or sometimes called “egg skin”
เอกสารอ้างอิง
เกียรติศักดิ์สรอยส ้ ุวรรณ. 2545. การฟักไขและการจ ่ ัดการโรงฟัก. คณะวิชาสัตวศาสตร์สถาบัน เทคโนโลยี ราชมงคล วิทยาเขตนครศรีธรรมราช, นครศรีธรรมราช. 230 น.
เฉลิมชัย สังข์มณฑล. 2554. คู่มือไก่ไข่. เกษตรสยาม, กรุงเทพฯ.
วรวิทย์วณิชาภิชาติ. 2531. ไข่และการฟักไข่. เค.ยู.บุ๊คเซนเตอร ็ ์. กรุงเทพฯ.
วิโรจน์จันทรัตน์. 2537. กายวิภาคและสรีระวิทยาของสัตว์ปีก. มหาวิทยาลัยแม่โจ, ้เชียงใหม่. สํานักงานเศรษฐกิจการเกษตร. 2551. สถติิการเกษตรของประเทศไทยปี 2550. ศูนย์สารสนเทศสานํ ักงาน เศรษฐกิจการเกษตร, กรุงเทพฯ.
อรวรรณ ชินราศรี. 2547. เทคโนโลยีการผลิตสัตว์ปีก. หจก. อภิชาตการพิมพ์, มหาสารคาม. อาวุธ ตันโช. 2540. การผลิตสัตว์ปีก. พิมพคร์ ั้งที่ 2. ภาควิชาเทคโนโลยีการผลิตสัตว์สถาบันเทคโนโลยีพระ จอมเกล้าเจ้าคุณทหารลาดกระบัง, กรุงเทพฯ.
Currently, Thailand is raising layer chickens. Widespread both natural and industrial culture. which the area is an important source of chicken egg production Thailand is mainly in the eastern region. followed by the Northeast, the North, the Central, the South and the West Bangkok and its vicinities, respectively. The provinces that produce the most eggs are Chachoengsao Province. followed by Nakhon Nayok Province Chonburi, Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya and Ubon Ratchathani, respectively.
laying hens
Chicken breeding is an important factor in the successful chicken farming business. so the babysitter Must choose the chicken breed according to the purpose of raising, such as choosing chicken breeds for egg production, etc. In the past, it was popular to raise purebred chickens, but the egg breeds that are popular in Thailand today are mostly chicken breed Almost all hybrids Which is a breed that has been selected and bred as well, such as fertilizing eggs, growing eggs, laying eggs, resistant and eating less food. There are 3 types of chicken breeds raised in Thailand as follows:
Purebred chickens are the chickens that have been selected and bred continuously by breeders until Successive offspring are similar in shape, size, color, etc. to their ancestors or fixed breed characteristics. Purebred chickens were once very popular. Because it is known as a hen that lays eggs. But later it has been improved. Breeding breeds with higher yields instead of purebred chickens have become less popular.
Until now, the chicken breed Has received little attention and is a commercial party. Because laying hens are popular with raising chickens from hybrids. Cross-breeding, which produces much better yields than purebred chickens. As for the purebred layer chickens that are still kept in Thailand, they are:
1.1 Rhode Island Red breed, also known as “Road Chicken”, originated live in the united states It is an old breed of chicken that is more than 100 years old by breeding and selection. from red Malay chicken Red Shanghai Chicken Brown horned hens, Cornis hens, Wyyan dots and Brahmas breed chickens. There are two types of Rhode Island Red, namely the rose comb type and the crested chakra (single comb). Which is a chicken that gives quite good eggs used to have a record of winning the egg-laying competition in Thailand is always
Characteristics of Rhode Island Red Crest Chak Chicken It is a semi-meat and semi-egg chicken. has been bred until there is a crest medium-sized crest It is quite long and deep. rectangular The general feathers on the body are brown, dark red, and the wing feathers and tail feathers are black and green. The skin and shins are very yellow. red-yellow mouth, red eyes, crest
Chakra 5-pointed, ear pads are red. The eggshell is brown. Medium-sized eggs, docile character, able to adapt to The environment is good. Egg laying begins at about 5 and a half months of age. Eggs are quite fecund, i.e. 280-300 eggs per year. Body weight when mature. Male weighs 3.1-4.0 kg. Female weighs 2.4-4.0. kg
In the past, in Thailand it was very popular to raise chickens of this breed. because in addition to yielding good results in both eggs and meat Strong, resistant, easy to raise and grow fast, but nowadays popular for use as a breeding ground in the production of hybrid laying hens Mostly hybrids To obtain a hybrid that can be gendered at birth by using a male Rhododendron mixed with a
bar. Plymouth Rock Female The resulting hybrids can be sexed at 1 day of age by looking at the difference in the color of the feathers, that is, the female chicks have black hair throughout the body. The male chicks have black feathers all over the body but have a white spot on their heads and when fully grown, the female hybrid chickens are the chickens that have all black feathers.
And the male hybrid chickens will have colored feathers throughout the body like a chicken. Bars by today’s commercial laying hens that provide brown-shelled eggs are Mainly from the crossbreeding of chickens. Rhode Island Red Crest with Bar Plymouth Rock Chicken The resulting hybrids will fertilize eggs. Eggs have brown shells and produce large eggs.
1.2 Barred Plymouth Rock breed, also known as “Chicken Bar”, is a Plymouth Rock chicken with bar colored feathers. It has black and white hairs alternating across the hair shaft, long body, crest, yellow mouth, reddish-brown eyes. The crest and earrings are red, the skin is yellow, the legs and toes are red. give brown-shelled eggs Start laying eggs at about 5 and a half months of age. Tolerant of environmental conditions. Males weigh about 3.6-4.3.
kg. Females weigh about 2.7-3.7 kg.
The Bar Plymouth Rock chicken breed originated in the United States. It is a semi-meat and semi-egg chicken. is a species Has been bred and selected around the year. 1865 by crossing Dominic male hen (Dominiqlue) and female hen Black Chochin (Black Java) used to be bred. The popularity of raising as laying hens for a while, about 30 years ago, but nowadays the mother is used to mix with the breeder. Rhode Island Red or New Hampshire breeds to produce hybrids are commercially selective, gender-selective at birth based on coat color, with females having black fur and fertile eggs. The male hybrids have a bar color.
1.3 Single Comb White Leghorn breed originated in Italy. It is the most popular breed that is widely kept among the small horn chickens together. This breed of chicken used to be popular as a chicken. eggs widely In the early days, there was an industrial laying hen. It is a light chicken breed that is small, agile, agile, has a fast growth. Full white fur, large 5-pointed crest, red crest, yellow mouth,
white earrings, yellow skin and hard face, ovulate quickly, fertilize, white shell eggs. effective in The change in diet is quite high. Tolerant of hot weather, start laying eggs at the age of about 4 and a half months, laying about 300 eggs per year, weight at maturity, males 2.2-2.9 kg, females 1.8-2.2 kg.
Currently, the white-horned, crested small-breed chickens are commonly used to cross breed 2 or more breeds. to produce chicken eggs Commercial hybrids that fertilize, grow eggs, and eat less. which meets the market demand
Hybrid Breeds (Hybrid Breeds) refers to laying hens that are produced by mixing two or more breeds of laying hens together. Because it is a specially mixed breed of chicks, the egg production company has developed and improved the breeding to be effective in yielding. Egg production is high and the quality meets the market demand, namely the fertilization of eggs. brown eggshell Large eggs and resistant eggs because it has been gathered together
This hybrid chicken has characteristic traits and includes detailed breeding information such as growth rate, feed intake. survival rate Ovulation
percentage The length of time for laying eggs, the size of the hens. The size of the egg, the color of the eggshell, etc., but this hybrid chicken must be fed with high-quality food. There is proper management such as weight control. food intake control lighting control throughout the sanitation and Good disease prevention as well.
As most of the hybrid chickens are bred by commercial layer breeding companies, the company will keep the source chickens and the breeding system confidential. for commercial benefits chicken present There are many hybrid eggs. Most of them were bred in the United States and in Europe. with a specific copyright In Thailand, private companies have imported broiler,
grandparent and parent chickens. Produce chicks and eggs for sale to breeders There are many varieties, such as AA Brown, Ross Brown, Hisex Brown, Isa Brown, Super Hard. Super Harco, Dekalb Voren, Hubbard Golden Commet, Shaver Starcross 579, Babcock B-380 (Babcock B-300), Babolna Tetra-SL, etc.
Principles for choosing a breed of laying hens to raise
Because chicken breed is one of the important factors in raising layer chickens successfully. Therefore, the selection of varieties Laying hens must be carefully considered. Don’t be fooled by the advertisements alone. The breeder must select the breed. By using observations and based on the following criteria for consideration
It is a good selection of chickens that have been specially selected as laying hens.
Looks good according to the breed and type of laying hens.
Produced from farms of good and reliable standards
High efficiency in egg production Long peak egg period, resistant eggs, large eggs and thick shells. 5. Has a high survival rate, is strong and can withstand the weather conditions of Thailand well. are considered and other varieties for comparison.
Structure of the Egg
The structure of an egg is made up of five major components: the egg shell and egg shell membrane, air cell, air space, egg white (albumen), egg yolk (yolk). ) and the origin (Germinal dise) as shown in Figure 1.
Shell The eggshell consists of two important layers within these layers. with many pores about 8, 000 Holes for passage of water and gas. In addition, bacteria May pass or penetrate through the holes in the eggshell as well. The newly released eggshell is usually clear, but becomes opaque when it dries. The outer surface of the eggshell is covered by a thin membrane called (Bloom or cuticle). After the egg comes out, this thin membrane dries quickly, causing it to close the pores in the shell completely. to prevent evaporation of water and gas from the eggs as well as to prevent the penetration of bacteria that may occur in the shell of the fish. The egg shell is more porous than the rest of the eggshell. During approximately 3 weeks of incubation of the mother egg, approximately 15% of the egg shell’s thickness has been evaporated by moisture or water. visible that is directly related to the volume of eggs for example A hummingbird’s eggshell is only 0. 06 mm The eggshell needs to be thick enough to hold the components inside the egg and to be brittle. enough to allow the embryo to penetrate easily.
Next to the eggshell, there is a thin egg membrane, which has 2 layers, which serve to cover the egg white and also Prevents egg components from invading bacteria. It also prevents the water from evaporating quickly from the egg. The outer shell and inner shell membranes are normally close together. Except at the obtuse ends of the egg bubbles, they are often far apart, creating an air cell that looks like a convex lens.
When the eggs are freshly hatched, there are no air cells at all until the egg cools down. It is an air channel that can be seen because the temperature of the egg that comes out of the new body. will have a temperature equal to Body temperature (about 107°F), which is higher than outside body temperature causing the temperature of the eggs to
gradually decreased, resulting in the components inside the egg to contract more than the egg shell, causing the inside of the egg to be Vacuum and air are drawn through the perforations at the obtuse end of the egg, thus creating air pockets. The size of the air pockets will increase over time. (Especially in hot and dry areas) The enlargement of the air pockets occurs from the evaporation of water and gas from the egg bubbles. Function to prevent shock that may occur from shock (Shock absorber) during embryonic development. within the first It is also the part that provides air for the embryo inside the egg that has incubated 21-28 days, which it will use its beak to penetrate the membrane of the egg to understand the air space inside the new egg to notice the white terminal part 2. Terminals are attached at both ends of the yolk (White cords). These terminals are called chalazae, which are twisted strips. Twisted strands of mucin fibers Contains proteins This special kalasa serves to hold the yolk in the middle of the egg.
The Shell Membranes and Air Space There are two membranes enclosed in the egg’s interior, which are loosely in contact with each other. The outer tissue will stick. tight to the shell part This means that the bark is embedded in the outer and inner tissues. During the incubation process, it was found that the elements inside the egg began to shrink. This is due to the evaporation of water from The fertilized egg and the development and maturation of the embryo require various nutrients contained within it. Egg eggs and for this reason cause the two tissues to separate from each other. obtuse area of the egg bubbles and forming air pockets However, the part of the air channel is an important component for The development of the embryo is enormous. Because it is the part that allows the embryo to move the body over time. prior to hatching
Egg White (The White or Albumen) Egg white is a half-solid, half-liquid protein. rather contain high water content. Flexible, acts as a shock absorbing and heat shield as well. The white meat can be divided into four layers: (1) Outer thin white (Layer of outer thin white or Fluid layer) (2) Middle thick white layer (Layer of thick white) (3) Inner liquid layer (Layer of inner thin white) and (4) Chalaziferous layer (Layer of thick white) which surrounds the egg yolk layer. in the end of the egg white at both ends side of the yolk It is shaped like a knot, resulting in a part called chalaza, which serves to hold the egg. Red is in the middle of the egg and allows the yolk to spin and twist around, the rest is Non protein solids.
The yolk The yolk is made up of layers that are dark and lighter, stacked in a circle spread out. The radius is within the yolk membrane. (Vitellinemembrane) is usually lighter than egg whites. and often stays above the point At the center of the newly released egg, the germ cell (blastoderm) is seen as a faint spot on the top surface. noticeable This fertilization point in an egg that has been fertilized with a male fertilizes and develops.
softer if in the right environment An egg with two yolks may be fertilized with sperm but usually does not hatch. Two yolks form in the same egg. May be a result of the ovum (Ovum) 2 eggs that occur. almost at the same time Infected eggs should be kept at temperatures below 10 °C to prevent The growth of the embryo within the egg is considered to be what allows the perpetual persistence of living things. especially in animals wings can be seen that The yolk contains a lot of nutrients that are essential for the growth of the embryo. which is more than the egg white (embryo maturation in the egg of some animals, such as the sei bird, takes only 2 weeks while the birds Emu lasts almost 8 weeks, the eggshell contains calcium carbonate. Most of it, about 93-98%, which will be used to build bones and other parts. of the body by the embryo in the egg In addition, the bark also has them. Small amounts of protein and some other minerals
Origin or growth point (The Germinal Disc) when hammering out the egg. will find that the skin On top of the yolk there is a white dot. which has a diameter of about 4 mm. The merger between one cell of the female gamete, or egg, and one cell of the germ cell. male or sperm Each cell contains only half the number of chromosomes (n) of normal somatic cells. The number of chromosomes is even (2n), and after the fusion of the egg and the sperm which is called the process Fertilization is a body cell with an even number of chromosomes (2n). Then the cell divides into 2 cells and continues to develop and divide. And the final result will develop into a chick further, in which the chicks, while inside the egg, rely on the elements inside the egg as food for growth.
Chemical composition of the egg (Composition of the Egg)
Most of the ingredients of an egg are Water and equal amounts of protein, fat and ash. The yolk is the part The highest nutrient concentration was only 50 percent water, as shown in Table 1.